This tutorial is a part of the Data Structures and Algorithms class:
- Linked list: high level vs. on RAM vs. on code
- Shallow copy vs. deep copy in Javascript
- Build Linked List data structure
- How to insert/delete/access/search data
- Doubly Linked List
- How fast to insert/delete/access/search data
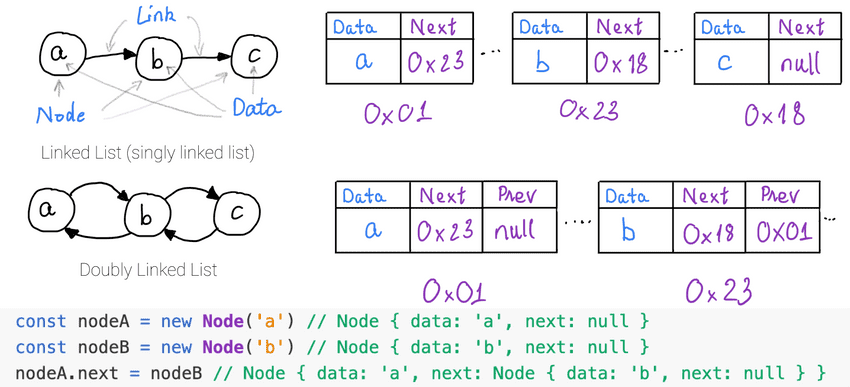
Linked List: high level vs. on RAM vs. on code
Linked List data structure:
- contains a
listofnodes,linkedtogether in alinear order. - each
nodecontains:dataand theaddressof the next node. - Real life applications: pre-determined waypoints for vehicles like: airplanes, satellites, shipping boats, self-driving cars, ..., implementation of stack, queue, ...
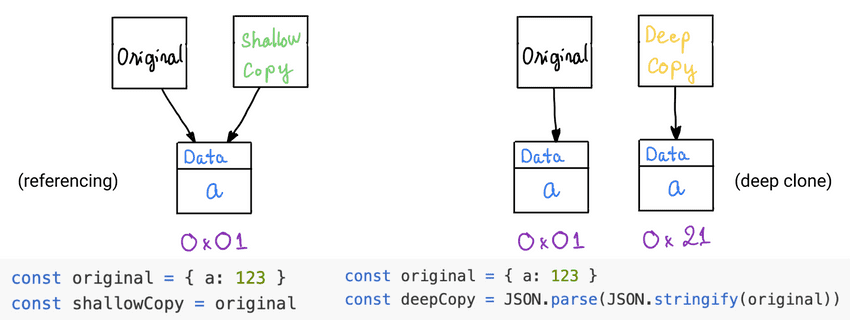
Shallow copy vs. deep copy in Javascript
In Javascript:
- assigning a new variable to an existing one means
shallow copy(also known asreferencing). In your code, two variables (original + new) are holding the same address to a memory space, which contains the data. shallow copywill have the same changes made on theoriginalvariable and vice versa.- only when the original variable is
reconstructed(reassigned to a new value), theshallow copywill have its own copy of the data.
lecture-10/shallow-copy-vs-deep-copy.js
let original = { a: 123 }
const shallowCopy = original
const deepCopy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(original))
console.log('original:', original) // original: { a: 123 }
console.log('shallowCopy:', shallowCopy) // shallowCopy: { a: 123 }
console.log('deepCopy:', deepCopy) // deepCopy: { a: 123 }
// modify original
original.a = 456
console.log('original:', original) // original: { a: 456 }
console.log('shallowCopy:', shallowCopy) // shallowCopy: { a: 456 }
console.log('deepCopy:', deepCopy) // deepCopy: { a: 123 }
// modify shallow copy
shallowCopy.a = 999
console.log('original:', original) // original: { a: 999 }
console.log('shallowCopy:', shallowCopy) // shallowCopy: { a: 999 }
console.log('deepCopy:', deepCopy) // deepCopy: { a: 123 }
// re-assign original
original = { b: 789 }
console.log('original:', original) // original: { b: 789 }
console.log('shallowCopy:', shallowCopy) // shallowCopy: { a: 999 }
console.log('deepCopy:', deepCopy) // deepCopy: { a: 123 }$ node shallow-copy-vs-deep-copy.js
original: { a: 123 }
shallowCopy: { a: 123 }
deepCopy: { a: 123 }
original: { a: 456 }
shallowCopy: { a: 456 }
deepCopy: { a: 123 }
original: { a: 999 }
shallowCopy: { a: 999 }
deepCopy: { a: 123 }
original: { b: 789 }
shallowCopy: { a: 999 }
deepCopy: { a: 123 }Build Linked List data structure
lecture-10/linked-list-data-structure.js
// structure of a node
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data
this.next = null
}
}
// build Linked List data structure
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null
this.length = 0
}
insert(element) {
const newNode = new Node(element)
if(this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode
} else {
let currentNode = this.head
while(currentNode.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
currentNode.next = newNode
}
this.length++
}
delete(element) {
let currentNode = this.head
let previousNode
// if the 1st node is the element to delete,
// point the head to the 2nd node
if(currentNode.data === element) {
this.head = currentNode.next
// else, keep examine each node to find the element to delete
} else {
while(currentNode.data !== element) {
previousNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
// found, link `next` of previous node to the next node
// (removing found element from the list)
previousNode.next = currentNode.next
}
this.length--;
}
search(element) {
let currentNode = this.head
while(currentNode && currentNode.data !== element) {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return currentNode
}
}
// create a linked list
const linkedList = new LinkedList()
console.log(linkedList) // LinkedList { head: null, length: 0 }$ node linked-list-data-structure.js
LinkedList { head: null, length: 0 }How to insert/delete/access/search data
lecture-10/linked-list-data-structure.js
// insert
linkedList.insert('a')
console.log(linkedList)
// LinkedList { head: Node { data: 'a', next: null }, length: 1 }
linkedList.insert('b')
console.log(linkedList)
// LinkedList { head: Node { data: 'a', next: Node { data: 'b', next: null } }, length: 2 }
// delete
linkedList.delete('a')
console.log(linkedList)
// LinkedList { head: Node { data: 'b', next: null }, length: 1 }
// search
linkedList.insert('c')
linkedList.insert('d')
linkedList.insert('e')
console.log(linkedList.search('e'))
// Node { data: 'e', next: null }
console.log(linkedList.search('f'))
// null$ node linked-list-data-structure.js
LinkedList { head: Node { data: 'a', next: null }, length: 1 }
LinkedList {
head: Node { data: 'a', next: Node { data: 'b', next: null } },
length: 2
}
LinkedList { head: Node { data: 'b', next: null }, length: 1 }
Node { data: 'e', next: null }
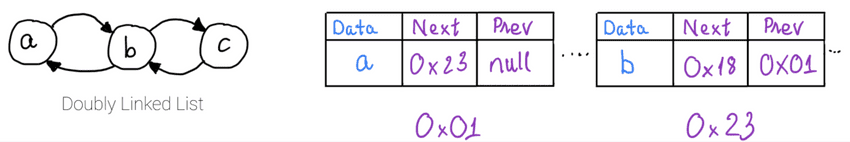
nullDoubly Linked List
The main difference between Doubly Linked List and Singly Linked List:
- Doubly Linked List: node-to-node travel is both way, head -> tail and tail -> head.
- Singly Linked List: node-to-node travel is one way, head -> tail.
How fast to insert/delete/access/search data
| Data Structure | Insert | Delete | Access | Search |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linked List + Doubly Linked List |
O(1): at head O(n): at random |
O(1): at head O(n): at random |
N/A | O(n) |
⬆️ Time complexity (worst case) per operation
Real life interview questions
- What is the Linked List data structure usually used for? Give 3 different examples.
- How do you insert/delete/access/search with Linked List data structure?
- What is the Time Complexity of Linked List data structure on insert/delete/access/search operation?
- Write your own Doubly Linked List data structure with these operations:
insert,delete,search. Make it O(1) access to bothheadandtailof the list. - Use what you've learnt to redesign Queue data structure to improve
dequeueoperation to O(1). - Solve Leetcode #21: Merge Two Sorted Lists.