This tutorial is a part of the Data Structures and Algorithms class:
- The best sorting algorithm has Time Complexity of O(nlogn)
- If we can sort, we (probably) can have top Time Complexity of O(nlogn)
The best sorting algorithm has Time Complexity of O(nlogn)
| Sorting algorithm | Time Complexity | |
|---|---|---|
| Merge Sort | O(nlogn) |
best |
| Quick Sort | O(nlogn) |
best |
| Bubble Sort | O(n^2) |
worst |
| ... | ||
| Full list of sorting algorithms from Wikipedia |
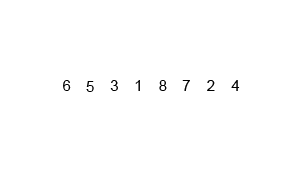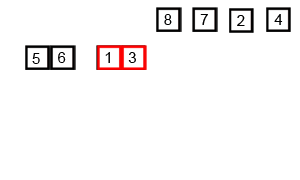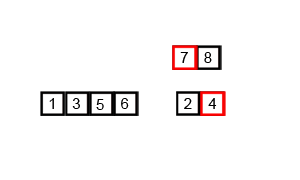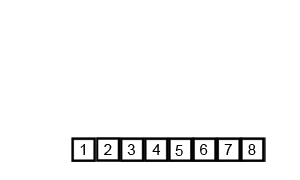
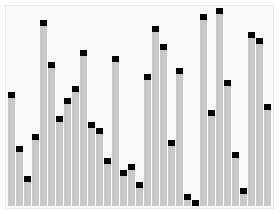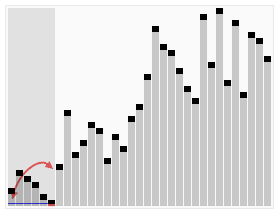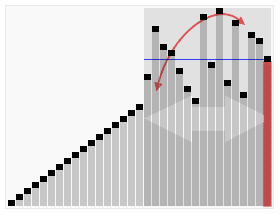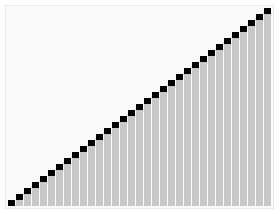
⬆️ Merge Sort, Time Complexity: O(nlogn)
⬆️ Quick Sort, Time Complexity: O(nlogn)
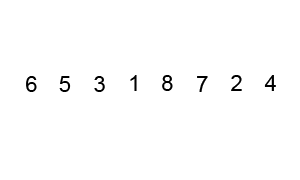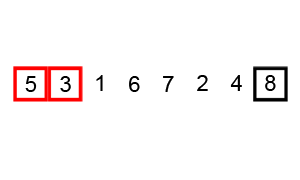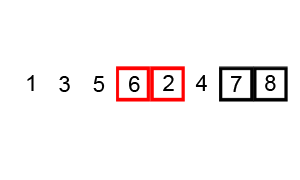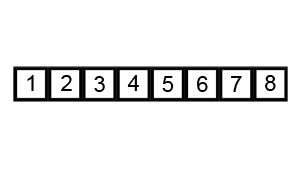
⬆️ Bubble Sort, Time Complexity: O(n^2)
If we can sort, we (probably) can have top Time Complexity of O(nlogn)
If your current solution has the Time Complexity of O(n^2) or more, sorting might be able to bring down Time Complexity lower or O(nlogn).
// Given an array of numbers, `find2` that add up to a given sum
// Brute force: O(n^2)
const find2BruteForce = (arr, sum) => {
// pick 1st num
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// pick 2nd num
for(let j = i + 1; i < arr.length; j++) {
}
}
}
// Sort + Binary Search: O(nlogn)
const find2WithSort = (arr, sum) {
// sort: O(nlogn)
arr.sort((a, b) => a-b)
// Binary Search nested in FOR Loop: O(nlogn)
// pick 1st num with FOR Loop
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// pick 2nd num with Binary Search
while(left <= right) {
}
}
}Real life interview questions
- Given an array of numbers, write function
find2numbers that add up to a given sum. - Given an array of numbers, write function
find3numbers that add up to a given sum. - Given an array of numbers, write function
find4numbers that add up to a given sum.
